Osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine is a degenerative pathology of the vertebrae and discs. It is generally accepted that lumbar osteochondrosis affects both the spine itself and the nerves and blood vessels. Therefore, the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine are divided into those that affect the spine itself - called vertebral / vertebral syndrome - and those that occur outside the spine, with the involvement of nerve and vascular structures - are called non-vertebral/ extravertebral syndrome. Extravertebral, in turn, is divided into reflex and radical syndromes. Since the word "syndrome" denotes a group of symptoms, it can be simplified and said that the symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine consist of three groups - vertebral, reflex and radical.
Vertebral symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
- Violation of the configuration of the spine (curvature).
- Lower back muscle tension.
- Violation of the mobility of the lower back.
- Local back pain.
Reflex symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
The main reflex symptom is back pain. It can be sudden or permanent. Pain occurs after physical activity or uncomfortable movement. For example, when turning, bending or lifting weights. There is muscle tension and stiffness of movements - more often in the morning. There are shots in the lower back or leg. The sensitivity of the lower extremities is reduced - numbness, goose bumps, piercing or burning. Changes in gait and coordination. Perspiration increases. The work of the intestines and bladder is often disturbed. There are malfunctions in the work of internal organs. Sexual function suffers. Sleep is disturbed due to pain. Mood swings, irritability and fatigue occur. Sometimes there is depression.
Factors that cause an exacerbation are physical exertion, prolonged uncomfortable posture, hypothermia, stress.
Reflex pain symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine, depending on the severity and localization of the process, are usually divided into low back pain, low back pain and lumbar sciatica.
- Lumbago (Lumbago)it is the sharpest pain. Provocation is an uncomfortable movement, sneezing, coughing. To relieve his condition, the patient involuntarily leans forward or bends to the side. Attempts to stand up cause new back pain.
- Lumbargia- aching "tolerable" pain, with flare-ups. Over time it develops into constant severe pain.
- Sciatica- Pain extending from lower back to leg.
Root symptoms of lumbar osteochondrosis
They appear due to the effect on the nerves coming out of the spine.
Many nerves come out of the spine. They are called spinal nerves. Each such nerve branches gradually and follows a specific area of the body with clearly defined boundaries. This area is called the zone of segmental innervation. Each vertebra, disc, nerve and belt is numbered strictly corresponding to each other. If the nerve is affected, the symptoms will appear in the zone of segmental innervation corresponding to this nerve, and not anywhere - in an arbitrary place.
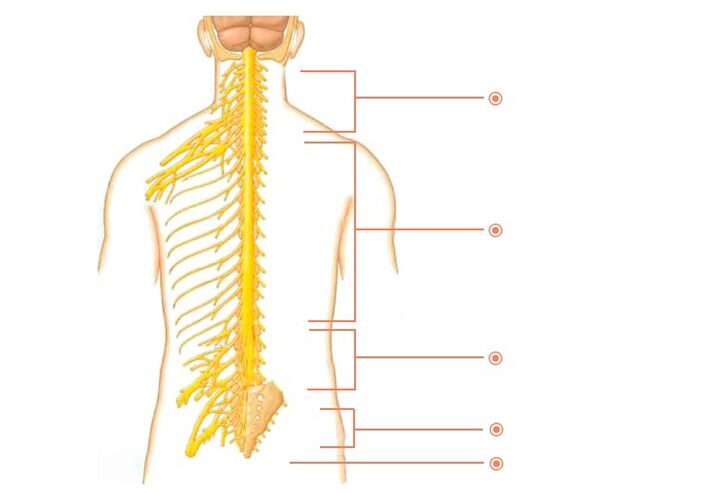
spinal nerves
The root symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine include:- reduction or loss of reflexes.
- muscular weakness;
- violation of sensitivity;
- root pain.
Not all parts of the lumbar spine are equally susceptible to pathology. The most mobile segments are most commonly affected: L3-L4, L4-L5 and L5-S1. According to the principle - "More movements - more wear. "
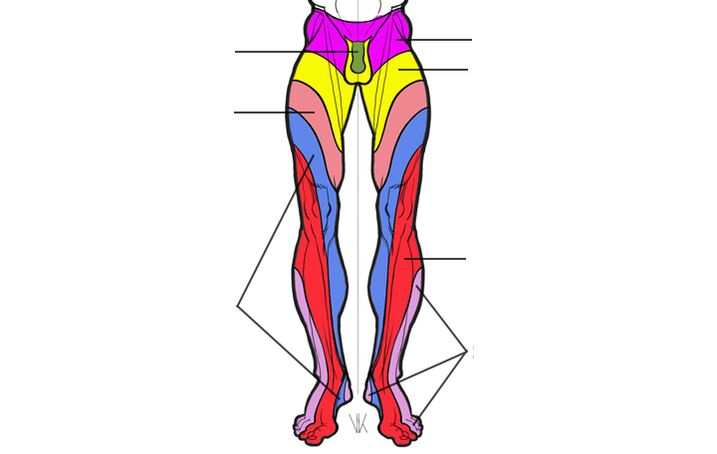
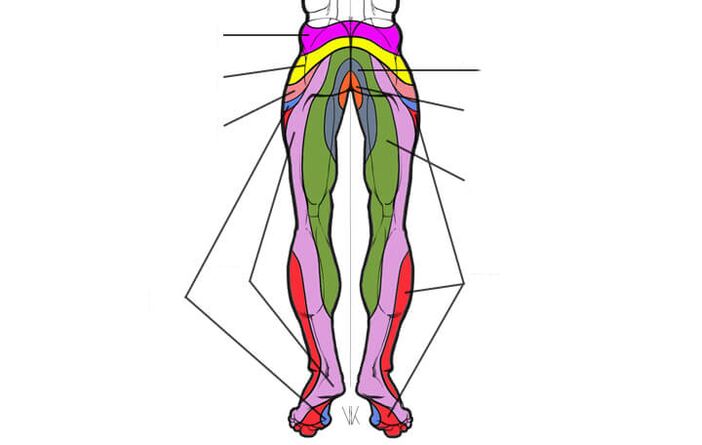
Belts of innervation of the lumbar parts
Osteochondrosis L3–L4- acts on the L4 spinal nerve. Main signs: weakness of knee jerk. Pain, numbness, and decreased sensitivity disrupt the front of the thigh.
Osteochondrosis L4–L5- acts on the L5 spinal nerve. Main signs: weakness in the muscles that raise the big toe and foot. It is difficult for the patient to continue standing on the heel. Pain, numbness and reduced sensitivity disturb the lower back to the buttock and thigh "along the line", then through the lower leg, gradually progressing to its front and ending in the first three toes.
Osteochondrosis L5–S1- acts on spinal nerve S1. Main signs: weakness in the calf muscles. It is difficult for the patient to continue standing on tiptoes. Pain, numbness and reduced sensitivity are felt from the buttock, then along the back of the thigh and shin, moving to the side of the foot and the little toe.
Sometimes, with lumbar osteochondrosis, not only the nerves, but also the root arteries can be affected. This threatens the development of the most dangerous pathology - spinal stroke, with serious consequences for a person - paresis and paralysis, as well as serious malfunctions of the pelvic organs.
Symptoms of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine:
- depends on the stage of osteochondrosis.
- aggravated by leaning and turning.
- more often they appear after 30-35 years.
- women are about 3 times more likely than men.
Of course, you noticed that the root symptoms are clearly defined, and the reflex symptoms are very vague and unclear. And as you know, anything without clear definitions serves as a convenient cover for professional weakness. This applies, among other things, to reflex symptoms and such a favorite concept among doctors as "age-related changes". Surely many of you are familiar with the situation when the doctor explained the problem with "reflex" or "age-related" processes. Most people at such moments rightly believe that the doctor simply cannot understand what is happening and tries to cover his incompetence in the fog of these "magic words".
There was once a popular saying: "Every accident has a name, a surname and a position. "Each disease has its own unique symptoms. And the doctor's duty is to know them clearly. And then you will not have to leave the fog and blame the osteochondrosis of the cervical spine for everything. Now you understand how important it is to find an experienced and qualified doctor. Both the correct diagnosis and the results of the treatment will depend on this.
When choosing a clinic, the main thing is to get to an experienced and experienced doctor.
Diagnosis of lumbar osteochondrosis
To date, there are many modern methods of diagnosing osteochondrosis through hardware. The most accurate of these are MRI and CT. But the main method is still clinical diagnosis - this happens when an experienced doctor compares data from at least three sources - from patient complaints, MRI results and the symptoms revealed by him during the examination. This allows you to make the most accurate diagnosis and create an effective individual treatment plan.
Treatment of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
As you understand, osteochondrosis is a real "bundle" of symptoms, unfolding, the doctor will save you from pain and agony. But it is not possible to eliminate the changes in the vertebrae and discs. Therefore, the words "treatment of osteochondrosis" must be understood correctly. If you are interested in eliminating pain and other suffering, then yes - it is very possible. And if you are conducting an academic discussion on the topic of returning the vertebrae and discs to their original appearance, "like a newborn child", then no, the past cannot be returned. You have to be realistic and then you won't fall for the scammers' bait.
Don't fall for the scammers' bait!
It is impossible for the vertebrae and discs to return to their original appearance!
What is the main method of treatment?
Soft manual therapy is the main type of treatment for osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine. It's like an antibiotic for pneumonia - you can't live without it. Other types—massage, medication, physical therapy, and exercise—are helpful.
How does gentle manual therapy work?
The nutrition of the discs is directly related to the muscles surrounding the lumbar vertebrae. In addition, the lumbar muscles themselves are one of the constituent causes of pain in lumbar osteochondrosis. Soft manual therapy is a special method that allows you to restore the muscles to their natural physiology, eliminate spasms, muscle clamps and improve disc nutrition.
The intervertebral discs are the only part of the body that does not have blood vessels and is nourished by the proper functioning of the muscles.
In addition, during manual therapy, the chiropractor:
- remove the load from the affected vertebrae and discs and distribute it properly
- relax the muscles and help them return to normal
Therefore:
Manual percussion mobilizes the body's internal forces and triggers self-healing mechanisms. The treatment is completely safe.
The clinic uses all soft manual therapy methods:
- release the patient from clamps
- improving movement power
- restores the motor functions of the body
normalizes blood circulation
The qualification of the doctors of any professional clinic allows you to freely use all these methods for the treatment of osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. Moreover, in each case we combine them, taking into account the synergy effect.
Synergy isn't just a bunch of different influences, it's the right order in combining methods. Synergy leads to additional quality of treatment. A simple example of synergy is our hands. How long does it take to snap a button? Seconds;! And if you do it with one hand, you can't manage it in a minute. That is, to act with two hands not twice as fast as one, but many times faster. And to hear the same music performed by individual instruments or by the whole orchestra together - is there a difference? This is the result of synergy - it makes it possible to do everything much stronger, more efficiently and faster, but at the same time - more carefully.
Complementary therapies - medications, massage, physiotherapy and exercise
Drug treatment.In the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, drugs of various spectrums of action are used. These are medications that relieve deep tissue swelling, inflammation, and pain. Medicines that improve blood circulation. In addition, drugs are used that help restore the damaged cartilage tissue of the disc and pressed nerves - chondroprotectors and B vitamins. Taking drugs, in combination with other treatment methods, if necessary, is prescribed by a chiropractor.
Massage.As you know, there is massage for pleasure and massage for therapy. Massage for pleasure is done in spas, and massage for therapy is done in medical clinics. In the clinic, medical massage is performed during a gentle manual therapy session. To increase the effectiveness of manual therapy and normalize metabolic processes - all this can be therapeutic massage!
Physiotherapy.There are many physical therapy methods that help manual therapy in the treatment of lumbar osteochondrosis, for example, ultrasound therapy, electrophoresis, laser, etc. A specific recommendation will be given by the treating chiropractor.
Physiotherapy- includes regular exercise to strengthen muscles. The main thing is to perform the correct exercises without sudden movements. During treatment at a specialized clinic, the doctor will recommend the necessary exercises. Pilates is the best option.
Prevention of osteochondrosis of the lumbar spine
To avoid relapses, create comfortable conditions for sleeping and working. Watch your weight and proper nutrition. Keep up your physical activity. But the main thing is not to neglect your health and not save on it. Don't let things go by themselves. After recovery, try to have at least one maintenance session of gentle manual therapy once every three to six months - this will reduce risk factors. Do not forget, neglected osteochondrosis leads to complications - disc protrusion and herniation. Remember: your health, first of all, you need!
Osteochondrosis of running leads to complications - disc protrusion and herniation.
Benefits of treating osteochondrosis in a specialized clinic:
- Guarantee of complete and specialized treatment. The word "full" is the key to our work.
- We consider each case individually and comprehensively - without formalities.
- Synergistic effect.
- Honesty and fair prices guaranteed.















































